DOMINANCE RELATIONS, VARIATION
Dominance relations:
Mendel gave the concept of dominance in the study of heredity. Mendel concluded that there were some traits that dominated over the other traits. But some experiments showed that all the traits in organisms do not follow Mendel's law.
For example:
It was found that, there are many traits which are controlled by more than one pair of genes. Co-dominance and incomplete dominance are two examples of such deviations from Mendel's law.
1. Complete dominance
2. Incomplete dominance
1. Complete dominance:
In complete dominance, one allele is completely dominant over the other allele.
Example:
Tall "T" is completely dominant over dwarf "t'. Therefore in heterozygous condition (Tt), tall hides the dwarf character.
2. Incomplete dominance:
In this case a given allele does not completely mask (hide) the character of a second allele. Actually they interact in such a way that heterozygous phenotype is a blending (mixing) of both. It is not according to Mendel's law. It is a deviation.
Example:
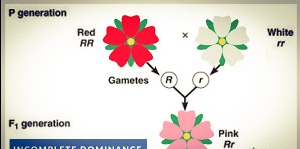
The inheritance of flower colour in Mirabilis jalapa (Four 0 clock plant) is an example of incomplete dominance. This plant produces two types of flowers red coloured (AA) and white coloured (aa).
When a red flowered variety is crossed with white flowered variety, the hybrid (F) is pink (Aa), an intermediate colour between the two parents. Thus the homozygote is either red or white but heterozygote is pink. When cross is made between pink flowers in Fz generation, the following groups results in.
Red flower = 1/4
White flower = 1/4
Pink flower = 2/4
This cross is shown as under.
Parents (P)Red flower + white
AA. aa
| |
Gametes....... A a
/
/
/
F1 (all identical) Aa. ( Pink flower)
F2. = F1 × F1
Aa × Aa
| |
A,a A,a
A a
AA Aa
A| Red Pink
a | Aa aa
pink white
3. Co-dominance:
Co-ordination is a deviation from Mendel's law. In this case two different alleles of a gene pair express themselves completely instead of showing a dominant recessive relationship. Thus heterozygous organism shows traits of both the parents. This is also against Mendel's law. Pure breeding means homozygous.
Example:
Example of co-dominance is the expression of blood group AB in humans. ABO has four different phenotypes which are due to specific antigen on the surface of RBC. The heredity of blood groups is based on various combinations of three alleles of one gene, symbolized as IA, IB and i. Both IA and IB alleles are dominant to the allele i. Therefore IA and IB alleles are co-dominant, both are expressed in heterozygote (IAIB) and the person has AB blood group and no one dominates over the other.
This can be shown as under:
VARIATION
Variation:
No two individuals resulting from separate fertilization are genetically identical not even twins. If you look to brother of the same parent, they will be different from one another especially in the height and colour of the eyes or hair.
Variation allows the survival of the fittest. Nature selects those varieties that are more competitive and more resistant to diseases. These varieties are capable of adaptation to the environment.
Variation and its sources:
The differences in height, size, shape, colour, habit, intelligence among individuals of the same species is called variation. The main sources of variations are:
1. Genetic recombination
2. Mutation
3. Environment and variation
1. Genetic recombination:
Genetic variations occur due to the following three Components of sexual reproduction.
a) Independent assortment of chromosomes
b) Crossing over
c) Random fertilization
a) Independent assortment of chromosomes:
The process of meiosis occurs for the formation of male and female gametes. As a result, the separation of homologous chromosomes takes place. New combination of chromosomes occurs in daughter cells. It is responsible for the genetic variation.
b) Crossing over:
Crossing over means sexual reproduction by means of sperms from male and egg of female. During prophase of meiosis, chromosomes have some genes from one parent and Some genes from the other parent.
c) Random fertilization:
Each gamete has a unique genetic composition. By random fusion of gametes, the organisms produced are different from all other species.
2. Mutation:
Any change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA is called mutation. Alleles arise by mutation. Any change in gene can alter gene product. If there is no mutation, there will be no biological evolution.
3. Environment and variation:
Scot pines have genes which enable them to grow to a height of 35 metre. But if it is grown in a small pot, it will grow short. It is due to limited space. It is an environmental variation.
complete dominance, incomplete dominance, codominance incomplete dominance example, incomplete dominance vs codominance, types of variation! variation examples, causes of variation what is variation class 10, importance of variation, discontinuous variation












0 Comments
If you have any doubts, please let me know